Cultures > Assyria
Assyria

Background
Assyria was a great empire and the first superpower to exist in ancient history. The Assyrians are credited with ruling over the largest empire to exist in ancient Mesopotamia, at its height covering over 750 hectares and encompassing everywhere from Nubia to Egypt to Babylonia and all of the rest of the cultures of Mesopotamia. Thankfully the Assyrians left a great deal of written material behind in order for us to study and figure out the facts and discern their history. The Assyrians leave a long and storied legacy that continues to exist into the present day.
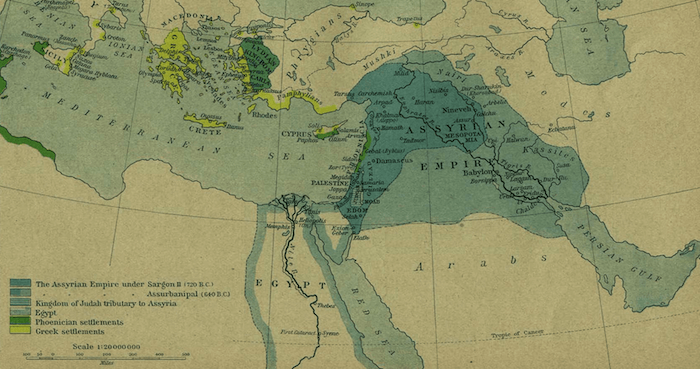
Assyrian Empire Map (750-625 BC) - Historical Atlas (1923)
The Assyrian Kings were known to be great builders and their capital existed at Ashur and then later at the city of Nineveh. It was actually at Nineveh that a great massive gardens and palace was built by the king. It would be this garden that Nebuchadnezzar II would copy to create his Ancient World Wonder, the Hanging Gardens of Babylon.
Assyria is a civilization that has origins stretching back into the furthest recesses of time and is broken up into three major periods, the Old Assyrian Kingdom, the Middle Assyrian Kingdom and the Neo-Assyrian Empire. While they can be classified as distinct political entities for the most part the day to day life of the average citizens along with the major culture and religion probably changed very little until the final collapse of the Assyrian Empire at the hands of neighboring Babylonia.
The Assyrian Empire would finally be brought down for good by a combined coalition consisted of many of the states and civilizations they had previously subjugated as vassals. Led by the Chaldean tribal leader named Nabopolassar along with the king of Media named Cyaxares. Following a series of battles known as the Revolt of Babylon, it would see the complete decimation of Assyria for good and allow the rise of the Neo-Babylonian Empire.
Origins
Assyria was built out of the remnants of the Akkadian Empire after it was crushed by both internal and external forces. The people of Assyria were largely Semitic like the Akkadians before them and actually used the Akkadian spoken and written language. It is interesting to note that later the Assyrians would later adopt the easier to use Aramaic language of the Achaemenid Empire.

Ashur Emblem Relief
Assyria was not always centered around the city of Nineveh though. When the empire first began its headquarters was in the city of Ashur, known to the Sumerians as Subartu. Ashur was located northeast of the fledgling city of Babylon. The city itself was named after the god Ashur in Assyrian culture despite other biblical myths to the contrary. This appears to be more in keeping with their belief system as the Assyrians later converted to Christianity and these accounts are only found in later texts.
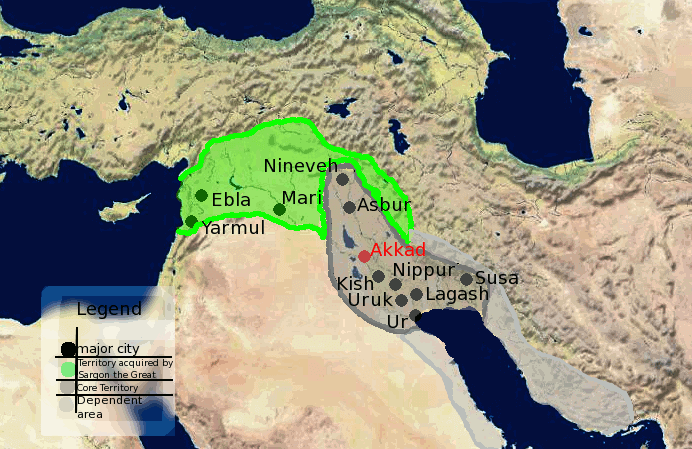
Akkadian Empire Territories Map
One of the major features of the early Assyrians was their development of a trade route between northern Mesopotamia and Anatolia (Asia Minor) which was controlled majorly by the Hittites. This trade network led the city of Ashur to become very wealthy and able to spread its influence throughout the region.
Assyrian Religion
Old Assyrian Kingdom
See Old Assyrian Kingdom.
The Old Assyrian Kingdom was a
Middle Assyrian Kingdom
Neo-Assyrian Empire
See Neo-Assyrian Empire.
The Neo-Assyrian Empire was a major Iron Age empire that existed between 911 BC and 609 BC. The Neo-Assyrian Empire was formed in the aftermath of the reforms of Tiglath-Pileser III in the 8th century BC which saw the power of Assyrian surpass that of neighboring Babylonia and Egypt.
The Neo-Assyrian Empire succeeded the Middle Assyrian period of the Late Bronze Age. During this period, Aramaic was also made an official language of the empire, alongside the Akkadian language.[4]Upon the death of Ashurbanipal in 627 BC, the empire began to disintegrate. In 616 BC, Cyaxares king of the Medes made an alliance with Nabopolassar against Assyria. At the battle at Harran (609 BC) the Babylonians and Medes defeated an Assyrian-Egyptian alliance, after which Assyria ceased to exist as an independent state.[5] Half a century later, Babylonia and Assyria became provinces of the Persian Empire.Assyria Collapse
See Assyria Collapse
Legacy
Despite the complete and utter collapse of their civilization, the people of Assyria actually continue to live on into the present day, although they aren't out conquering too much. In fact many Christian faith Assyrians are known to live in Iran, Iraq and elsewhere throughout the modern region. In fact their survival is currently threatened by the rampant civil wars that have plagued the Middle East for years. At its height the Assyrian Empires were the greatest in all of Mesopotamia, surpassing that of the previous Akkadian Empire as well as Babylonia and that of Sumer.
In fact, it should be noted that even during the time of Herodotus (484–425 BC), nearly all of Mesopotamia was still considered Assyria. The early study of Mesopotamian culture was also known as Assyriology until recently as we did not originally know about the Sumerians and the Akkadians.
The Assyrians were well known as primary sources in many of the Greek and Roman volumes which goes to show how widespread and influential the Assyrian culture was during the ancient period. It is because of these works that researchers are able to understand a great deal about Assyrian culture as well as translate the Akkadian language that was primarily used throughout the empire.
Translation of Akkadian
Nazi Comparison
See Nazi Comparison
Assyrian King List
The list of Assyrian Kings is a relatively unbroken chain of linage that dates back several hundred years during the bulk of the Assyrian Empire. It is important to note for how long this single linage was able to persevere for despite what was going on in the rest of the ancient world at the time.
The King List is known from several different tablets and fragments that can be put together to form a cohesive chain of lineage.

Syria was called Phoenician for a time then Aram. Then Ashur-yia based out of Assur that became an empire that took over the entire region of Aram/Phoenician. The Romans called the entire Assyria, and then divided into Assyria and Syria where Aram used to be. It also was called Coele-Syria. Arabic language brought to Syria by the Arabic invasion after the Islamic conquests of AD 600.