Cultures > Sumer
Sumer
Background
Sumer was one of the oldest civilizations that existed in Mesopotamia and one of the original six of the Cradle of Civilization theory. There is some debate between researchers of where and when the civilization exactly started, but most agree it was somewhere on the Persian Gulf. The first recovered human settlements grew up along the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers around 6,000 BC and were populated by a non-semitic people called the Sumerians. These settlements soon became independent and autonomous city-states with their own unique religious and cultural identity.
Eventually all of the city-states together led to the development of the civilization of Sumer. The loose collection of city-states often ruled by the most powerful priest-king lasted until about the 23rd century BC when it was conquered and incorporated into the Akkadian Empire. The ancient Sumerians started the first group work projects that involved draining the marshes and otherwise altering the environment to develop a larger human settlement.
They also were responsible for the development of different industries such as pottery, masonry, metalwork, leatherwork and weaving. These developments show a sophisticated interaction between humans that had decided to settle down and adopt agriculture and begin creating cities. The Sumerians were in fact non-Semitic people while the Akkadians to the north of them were Semitic people. The name Sumerian actually comes from the Akkadian word for these people.
The ancient Sumerians spoke and wrote a unique language called the Sumerian language, with their written language called cuneiform. In fact, one of the worlds first known fusions of language into the concept of bilingualism was established in connection with the neighboring Akkadian Empire. The Sumerian civilization at its height included approximately 800,000 to 1.5 million inhabitants. There were about 27 million people in the entire world at this time so this was a significant percentage.
Origins
See
Origin Myth
See
Ubaid Period
See Ubaid Period
Uruk Period
See Uruk Period
Early Dynastic Period
See Early Dynastic Period of Sumer
Akkadian Empire
See Akkadian Empire
Under the leadership of Sargon the Great, the Akkadian Empire achieved the zenith of its power. Around 2270 BC the Akkadians managed to conquer Sumer in the Battle of Uruk and incorporated it into their empire. Elam would be conquered as well and Sargon would control a uniform empire from the Mediterranean Sea to the Persian Gulf as well. There is a mixture of Akkadian and Sumerian language at this point. Some tablets are written purely in Old Akkadian, while official and administrative tablets continue to be written in cuneiform by the scribes.

Sargon the Great Bronze Head
It appears that both Akkadian and Sumerian languages co-existed until about 1800 BC. At this point it appears though that Sumer was known to be the language of the scholars and the scribes while Akkadian was the common spoken language.
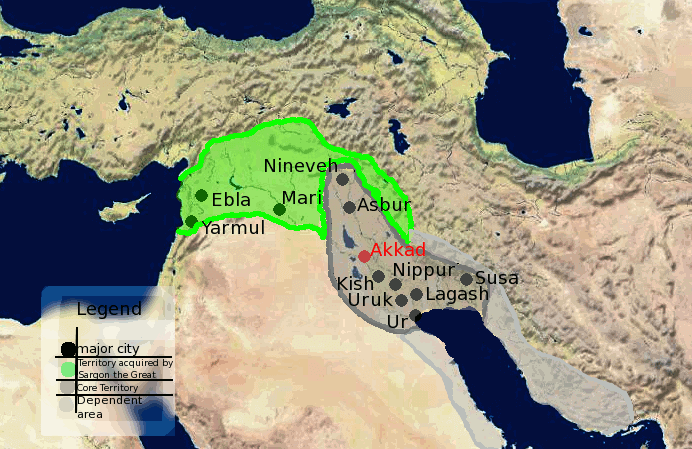
Akkadian Empire Territories Map
You can learn more about the Akkadian Empire here.
Gutian Invasion
See Gutian Invasion
3rd Dynasty of Ur
Sumer Legacy
See Sumer Legacy
Sumerian King List

Sumerian King List
| King | Reign (Short Chronology) | Reign (Long Chronology) | Dynasty |
| Alulim | Ante-Diluvian King | ||
| Dumuzid | Ante-Diluvian King | ||
| En-men-dur-ana | Ante-Diluvian King | ||
| Ziusudra | Ante-Diluvian King | ||
| Etana | 1st Dynasty of Kish | ||
| Enmebaragesi | 1st Dynasty of Kish | ||
| Enmerkar | 1st Dynasty of Uruk | ||
| Lugalbanda | 1st Dynasty of Uruk | ||
| Dumuzid | 1st Dynasty of Uruk | ||
| Gilgamesh | 1st Dynasty of Uruk | ||
| Meskalamdug | 1st Dynasty of Ur | ||
| Mesannepada | 1st Dynasty of Ur | ||
| Puabi | 1st Dynasty of Ur | ||
| Enshakushanna | 2nd Dynasty of Uruk | ||
| Ur-Nanshe | 1st Dynasty of Lagash | ||
| Eannatum | 1st Dynasty of Lagash | ||
| En-anna-tum I | 1st Dynasty of Lagash | ||
| Entemena | 1st Dynasty of Lagash | ||
| Urukagina | 1st Dynasty of Lagash | ||
| Lugal-Anne-Mundu | Dynasty of Adab | ||
| Kubaba | 3rd Dynasty of Kish | ||
| Lugal-zage-si | 2294-2270 BC | 3rd Dynasty of Uruk | |
| Sargon the Great | Dynasty of Akkad | ||
| Tashlultum | Dynasty of Akkad | ||
| Enheduanna | Dynasty of Akkad | ||
| Rimush | Dynasty of Akkad | ||
| Manishtusu | Dynasty of Akkad | ||
| Naram-Sin | 2254–2218 BC | Dynasty of Akkad | |
| Shar-Kali-Sharri | Dynasty of Akkad | ||
| Dudu | Dynasty of Akkad | ||
| Shu-turul | Dynasty of Akkad | ||
| Puzer-Mama | 2233-2218 BC | 2nd Dynasty of Lagash | |
| Gudea | 2144-2124 BC | 2nd Dynasty of Lagash | |
| Utu-hegal | 2116–2110 BC | 5th Dynasty of Uruk | |
| Ur-Nammu | 2047-2030 BC | 3rd Dynasty of Ur | |
| Shulgi | 2029-1982 BC | 3rd Dynasty of Ur | |
| Amar-Sin | 1981–1973 BC | 3rd Dynasty of Ur | |
| Shu-Sin | 1972-1964 BC | 3rd Dynasty of Ur | |
| Ibbi-Sin | 1963-1940 BC | 3rd Dynasty of Ur |